Contents
Bluetooth Low Energy: The Ultimate Guide on BLE From CTO
Published: April 29, 2024
20 min read
In this article, you'll learn:
1
📚 General BLE Facts
2
⚙️ BLE Technical Facts
3
🤖 BLE FAQ: Beacons and iBeacons
4
🗂 Our Expertise in BLE Integrations
5
💡 Takeaways
To start with, Bluetooth was initiated as a short-range technology to replace nodes and wires as a connection method. According to Statista the current number of shipped Bluetooth devices isn’t only presented in billions but is also growing continuously from year to year. Thus proving that the relevance of Bluetooth technology isn’t going to leave global markets in near future.
BLE Ultimate Guide (image by Andrew Rosek)
Bluetooth as technology exists in two types:
- Bluetooth Classic emphasizes continuous connections and transferring bigger amounts of data. In the product world, it’s represented by Bluetooth enabled devices, such as wireless speakers, headphones, keyboards, and interactive car systems.
- Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) emphasizes transferring lower amounts of data with energy efficient consumption providing an increased battery level for Internet of Things (IoT) products and accessories. In practice, it’s represented by small sensors and products compatible with BLE technology from various healthcare, fitness, and smart home systems.
Despite BLE devices being relatively new to the market, the Bluetooth SIG (Special Interest Group) report states that 1.8 billion BLE single-mode devices will ship in 2024 alone.
In this article, the CTO of Stormotion, Oleksii Bulavka, will share his knowledge about Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE). We’ll take a deeper look specifically at the basics of BLE, determine its technical characteristics, notice both the benefits and limitations of BLE products, and provide the answers to the most frequently asked questions before integrating it into your project.
📚 General BLE Facts
In this section, we'll cover the essentials of Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), including its definition, advantages, and limitations. We'll also discuss its relationship with classic Bluetooth, network setup, and similar wireless protocols.
What is Bluetooth Low Energy?
Bluetooth Low Energy is a wireless technology introduced in Bluetooth 4.0, with the purpose of creating connections that compared to the Classic Bluetooth technology:
- require low energy consumption;
- require long battery life;
- require lower cost;
- operate with infrequent data transfers.
What is Wibree?
Wibree is a technology with extremely low power consumption and a 10-meter range which is known as the first version of Low Energy Bluetooth. In 2009 it was rebranded as Bluetooth Low Energy and still functions under this name.
Bluetooth of any type plays a crucial role in developing and connecting IoT applications (image by Josh Warren)
The Advantages of BLE
- Accessibility. Nowadays almost every phone has an integrated BLE module making features of wireless connection wide open for every smartphone-like device owner. Besides, Bluetooth Low Energy technology is compatible with integration in devices that don’t require any apps for maintaining quality connections with various products. Hence, its accessibility is not only defined by being integrated into phones and tablets.
- Low power requirements. Along with transmitting data in small amounts, there’s another thing that lets BLE be the lowest power consumer amongst the candidates. Key optimization in conserving power is achieved by keeping the signal transmission off whenever it’s not used.
- Low elements cost. Among the BLE analogues the original technology boasts with low prices for chipsets, modules, and other components. Thus granting a cost effective option for the development to surpass any competitor existing.
- Free specification documents. The most notable advantage of Bluetooth Low Energy is that any specification document you may need can be easily found and downloaded from the official Bluetooth website. While some technologies require considerable payment for access to the documentation, BLE shows you that it is free to use for everyone.
The Limitations of BLE
- Limited range. There are several factors that lead to BLE’s short distance. First of all, the BLE frequency spectrum is vulnerable to the obstacles between the connected devices, making it yet impossible to implement connections exceeding 100 meters. And the other factor that complicates the long-range connections includes all the issues with a BLE antenna such as device orientation and physical location.
- Low data rate. Bluetooth Low Energy can’t be used to transfer data of more than Bluetooth basic rate of 1 or 2 Mbps as, for example, cellular and wifi technologies can handle. One of the causes is the requirement of Bluetooth Low Energy specification for a 150 ms signal gap between the packet transmission along with the transmission power being dependent on the connection range.

An example of BLE application to control heat level of the infra-heated vest (image by Ten Times Better)
Are BLE and Classic Bluetooth Devices Compatible?
Despite sharing the brand and specifications, Classic Bluetooth and low power Bluetooth aren’t compatible, a consideration important in the prototyping steps in IoT. It means that it’s impossible to connect devices directly.
Is there a Way to Make Classic Bluetooth and BLE Compatible?
To avoid Bluetooth LE vs Classic compatibility issues many smartphone-like gadgets tend to implement both of these technologies thus enabling communication with every side. Smartphones with such Bluetooth chipsets are called Dual Mode Bluetooth devices and are able to work with both Bluetooth Low Energy and Bluetooth Classic. According to the Bluetooth SIG report, each key platform device supports BLE Bluetooth and Classic Bluetooth.
Which One is Better: BLE or Bluetooth Classic?
Based on the experience of our CTO, it’s impossible to say which of the technologies is “better” or “worse” in general. The answer depends on your needs: whether you need to have a continuous data transfer, transmit large data packets, have the possibility to frequently recharge your device, etc.
Let’s see some examples of goals and determine the technology that fits better in distinct cases:
📱 Task examples | 📳 Suitable technology |
|---|---|
Motion sensors | BLE |
Wearable pedometers, heart rate monitors | |
Baby monitors, small walkie-talkies | |
Smart House sensors | |
Smart sensors for cars | |
Applications with a file-transferring feature | Bluetooth Classic |
Applications with a quality audio streaming feature | |
Wireless PC peripherals | |
Printer-like peripheral machines |
What is a Bluetooth LE Device Network?
Let’s talk about the main use cases of BLE enabled devices.
Applications | Use Cases |
|---|---|
Consumer electronics | Our smart watches, fitness devices, and other smart appliances which monitor our heart rate, steps, and other activities are compatible with our mobile phones, tablets, and laptops thanks to BLE technology. These Bluetooth LE devices, which often have low power consumption due to their sleep mode feature, prioritize basic functions like step tracking, heart rate monitoring, or blood pressure monitoring. Constant Bluetooth transmission of data to a paired phone would drain battery power quickly. BLE helps increase the time during which these devices work, making it an ideal solution. |
Audio devices | While we're accustomed to wireless headphones primarily using Bluetooth Classic, a recent advancement in Bluetooth LE device is LE Audio. This innovation brings several benefits, such as improved audio quality, reduced power consumption, and compatibility with hearing aids, distinguishing it from traditional Bluetooth technology. |
Smart house system | Bluetooth Low Energy devices play a significant role in the home automation market, facilitating the operation of various devices such as smart lights, smart locks, thermostats, and temperature sensors. These devices leverage BLE to offer functionalities like remote control, automation, and monitoring of humidity, temperature, and other environmental factors, enhancing convenience and security for homeowners. |
Healthcare management | Emerging smart contact tracing systems use BLE technology to combat the spread of infectious diseases. Rather than relying on manual data reporting, these systems continuously scan BLE tags or smartphones to anonymously identify individuals who may have been in close contact with an infected person. This approach was widely used during COVID-19 pandemic. |
Medical facility management | Medical smart devices, such as fall detection systems with BLE tags and motion sensors, are valuable in settings like nursing homes. Upon detecting a fall, these tags use location based services to pinpoint the person in danger and automatically send alerts to nurses. |
Asset tracking | BLE tags are not limited to tracking people in need. This technology can be used in different industrial scenarios, such as cargo tracking or inventory maintainance. |

Smart home systems utilize BLE technology to enhance comfort levels (image by Mostafizur Rahaman)
What are the Analogues of BLE?
Just like any other technology in today’s vast tech world, there will always be competitors. A competitive factor not only opens up a wider set of options to choose from but also lets the technologies prosper and evolve more among the analogues.
Competitive technologies:
- Z-Wave. A wireless protocol that’s represented as a mesh network with LE radio waves primarily used for home automation.
- ZigBee. A specification for creating personal area networks with the use of low-power radios. Presented as a mesh network, it’s responsible for low-power wireless connections in home automation and healthcare data management.
- Thread. A low-power mesh networking protocol based on IPV6 for Internet of Things product development. The main focus of this technology is providing outstanding security standards and being future-proof.
Let’s recap the given information 👇
- What does BLE mean? This abbreviation is short for Bluetooth Low Energy, which is a wireless communication technology designed for short-range communication between devices with low power consumption requirements.
- BLE offers several advantages, including widespread accessibility, energy efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and freely available specification documents. However, it faces limitations such as a restricted operational range and limited data transfer rates.
- What is Low Energy Bluetooth and Classic Bluetooth cooperation? Despite common Bluetooth branding and specifications, they aren’t directly compatible. Dual Mode Bluetooth devices bridge this gap, enabling communication between the two technologies.
- What is BLE superiority over Classic Bluetooth? There isn't a definitive superiority between BLE and Classic Bluetooth; rather, their suitability depends on specific requirements. While BLE needs less energy to transmit data, Bluetooth Classic may be preferred for continuous data streaming and higher data rates.
- BLE finds applications in various sectors, including consumer electronics, audio devices, smart house systems, healthcare management, and asset tracking, owing to its energy efficiency and reliable Internet connectivity.
- Analogues of BLE include Z-Wave, ZigBee, and Thread, offering mesh network capabilities and low-power radio waves for home automation and IoT devices development.
⚙️ BLE Technical Facts
In this section, we’d like to talk about the main technical characteristics of Bluetooth Low Energy. From its architecture to the limits of device connectivity, we'll illustrate what makes BLE a versatile and widely adopted wireless communication technology.
Frequency spectrum | 2.4 GHz |
Minimal time to send data | 6 ms |
Maximum radio data rate | 2 Mbps (Bluetooth 5) |
Connection range | Depends on environmental conditions, selected range mode, and used features. The regular range is 10-30 meters, however, under ideal conditions Bluetooth version 5 LE products may connect through about 400 meters |
Security and encryption | In CCM mode - 128-bit AES |
Peak current consumption | less than 15 mA |
Latency (non-connected -> connected state) | 6 ms |
What is Bluetooth Low Energy Architecture?
As stated by Oleksii, the BLE architecture is the network and organization of components within the BLE protocol stack or protocol suite. It consists of three main layers.
-
The application layer. It serves as the direct interface with the user and encompasses the application logic, user interface, and overall application architecture.
-
The host layer. It includes multiple protocols and profiles:
- Attribute Protocol establishes rules for accessing data, and defining attributes' structure and operations.
- Security Manager Protocol ensures secure device communication and addresses privacy. It validates and performs authentication during the pairing process. Additionally, it can deter detrimental tracking of a device’s Bluetooth address by concealing it.
- Logical Link Controller and Adaptation Protocol (L2CAP) acts as a protocol converter and handles standard BLE packet fragmentation.
- Generic Access Profile (GAP) manages BLE device communication, covering roles, advertising, and connection establishment.
- Generic Attribute Profile (GATT) facilitates attribute data transfer between devices, with a client-server model for read/write operations.
- The controller layer. The physical component of BLE firmware, the controller decodes signals and operates on the 2.4GHz bandwidth, dividing it into 40 channels for data transmission and advertising. The controller layer also comprises the physical and link layers, which manage how devices communicate.
- The physical layer denotes the radio hardware utilized for communication and data modulation/demodulation.
- The link layer serves as an interface between the physical layer and higher levels, interacting with the radio through an intermediary level known as the HCI (Host Controller Interface) layer. It handles radio state management and ensures adherence to the timing standards specified by Low Energy Bluetooth devices.

Using BLE technology, smart toothbrushes allow users to track recent brushing activity (image by Sam Pietrzak)
Are BLE Versions Backward Compatible?
Yes, Bluetooth Low Energy versions are backward compatible with each other. However, the features that were released in the newest versions won’t be supported by the older ones.
As an example, a BLE device with a Bluetooth 4.1 can easily be connected to a BLE device with Bluetooth 5.0, yet without access to the newest features of the 5-th version.
When working with Android BLE, developers must consider compatibility issues to ensure smooth connections across different Bluetooth versions.
Can BLE Products Stream Audio?
Before the release of the Bluetooth 5.2 update, Bluetooth LE devices didn’t support audio devices. With the use of custom implementations, there was a way to make audio streaming possible, however, it was never about achieving a good quality sound. After Bluetooth 5.2, audio transmitting finally became possible with many upgrades and specifications awaiting in the future.
Protocols such as Bluetooth and ANT are pivotal in supporting diverse use cases, including real-time audio streaming.
How to Power BLE devices?
Bluetooth Low Energy is a technology for maintaining faster connections with low power consumption. It's quite typical for a BLE device to operate for a year on a single battery, which showcases how IoT helps in manufacturing by reducing energy consumption and extending device lifecycles. Still, there’re various sources to power such products, underscoring the need for developers to understand how to build companion apps with high power efficiency, especially when developing a health and fitness app that relies on real-time data from BLE sensors. The most common power sources for BLE’s battery life are:
- Coin Cell Batteries
- Lithium Batteries
- Rechargeable Lithium Batteries
- Alkaline Batteries
Which makes it crucial to understand how to build battery management software to maximize performance.
What Certifications are Required for BLE Products?
Considering that Bluetooth Low Energy radios in fact are Radio Frequency (RF) transceivers — the needed certifications depend on the country where the device is going to be used. Besides the certifications, it’s also required to get an End Product Listing with the Bluetooth SIG, which is a critical step in the Bluetooth Low Energy development process. Some examples:
- European Region — CE certification
- Canada — IC certification
- The US — FCC certification
Is an App a Necessity for BLE?
Communicating and managing Bluetooth Low Energy products, such as those utilized in IoT in smart farming, is often maintained via a specialized app for iPhones or Android devices. Thus, an app is the most common way for managing BLE connection requests, and a BLE app development company can ensure a seamless connection experience, however, connecting devices directly is also practically possible. For example, Web BLE implementation allows for direct interactions with BLE devices through web browsers. We at Stormotion experienced the development of a heart-rate sensor with a direct connection to an exercise machine.
How Many Devices Can Be Connected to BLE Simultaneously?
Bluetooth Low Energy protocol is based on a Master (Central) and Slave topology, a Master can create a connection with multiple peripherals simultaneously as well as be the Slave and the Master at the same time. The peripheral device transmits timed advertising packets, while the central device scans for and utilizes these data to locate the peripheral device. A practical limit for the Central device — is supporting up to 20 peripherals connected.

An example of how a BLE device is connected to IoT applications (image by Adam Kalin)
However, the practical number stated before only shows the BLE capabilities in general, but this limit may be different for some cases. It depends on the application-specific aspects that define the number of simultaneous connections in particular cases. Such aspects are primarily:
- the limits set by the physical layer (the controller itself);
- limitations of the host OS.
Experimentally it was determined that a Samsung Galaxy S9 as a BLE Central can support up to 8 simultaneously connected devices. While the iPhone 8, for example, managed to connect up to 10 such products.
According to Microsoft Q&A, when it comes to connecting Bluetooth Low Energy to Windows it works as follows:
- BLE devices in connections have three different activity statuses: “paired”, “connected” and “transmitting”. A device can have one, two or three active statuses at the same time. For example, it can be paired and connected but not transmitting or can simultaneously be paired connected and transmitting.
- The devices in terms of communication can be hosts and clients. For example, speaking about connecting wireless peripheral devices to a PC, the first ones act as clients and the PC itself represents the host side.
- Host devices are able to support up to 7 products with a “connected” status and as many as needed “paired” devices.
- Client devices play a peripheral role and support only 1 connection and up to 5 “paired” devices.
Let’s summarize the technical facts about BLE 👇
- BLE operates within the 2.4 GHz frequency spectrum. Its connection range varies, typically spanning 10-30 meters, but without interference, products with Bluetooth 5 LE may connect up to approximately 400 meters.
- The BLE architecture comprises three primary layers. The application layer directly interacts with users. The host layer manages data access, security, and standard BLE packet handling. The controller layer divides the 2.4GHz bandwidth into 40 channels for data transmission and advertising.
- BLE versions are backward compatible, allowing connection between devices of different versions; however, older ones may not support the introduction of newer features in the latest versions.
- Prior to the Bluetooth 5.2 update, BLE devices lacked support for audio streaming. The Bluetooth 5.2 update introduced enhancements for quality audio transmission, addressing previous limitations.
- While specialized apps for iOS or Android devices are commonly used for managing BLE connections, direct device connections are also feasible, depending on the application requirements.
- BLE supports a Master (Central) and Slave topology, allowing a practical limit of up to 20 peripherals connected to a central device. However, actual connection limits may vary based on device and operating system specifics.
🤖 BLE FAQ: Beacons and iBeacons
In this section, we'll explore Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) technology and its application in beacon systems like iBeacons. We'll cover what BLE beacons and iBeacons are, how they work, and their differences. You'll also learn about their practical uses and the security measures in place.
What is a BLE Beacon?
Bluetooth beacons are a type of Bluetooth Low Energy device that’s presented as a wireless hardware transmitter. The main point of such beacons is to broadcast their identifier to various smartphone-like nearby devices within a close range to take control of them and perform actions like launching an app, opening an information page, or sending a notification.

An appearance of beacons presented by Estimote (image by Estimote)
What is an iBeacon?
iBeacon is an Apple protocol based on BLE proximity sensing that possesses a set of features similar to a Bluetooth LE protocol stack.
What is the Difference Between a BLE Beacon and an iBeacon?
Practically, to send information about the distance between connected products to a device, iOS delivers the actual calculated distance, while Bluetooth Low Energy relies on the RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator). Thus, in an iOS case, the estimated distance won’t depend on the device manufacturers and will be equal regardless of the device version.

The “inner world” of the beacons presented by Estimote (image by Estimote)
How Do BLE Beacons Work?
Let’s introduce ourselves to a Beacon world step-by-step:
- There is a small device called “Beacon” that is constantly transmitting radio signals.
- Devices nearby (smartphones, tablets, etc.) supported by Bluetooth Low Energy detect the transferred signal.
- The signal gives your device its ID number, saying “Here I am!”.
- Your device sends the ID it got earlier to the cloud server.
- The server processes the given ID and determines what action lays behind the assigned number and responds according to the scenario.
- The result could be any action pre-programmed before!
What Security Protocols Should Have BLE Beacons?
Two popular types of Beacon attacks can affect your mobile product:
- Beacon Spoofing. The attacker detects the Beacon ID of your device and creates a clone that behaves the same. The application of such a technique is quite obvious. The attacker can place the duplicate in other places, fooling your mobile app and user.
- Beacon Hijacking. The attacker detects the Beacon ID of the entire Beacon network you've invested resources into. This allows them to build another application, even a competitor, relying on the same Beacons.
Oleksii explains that the effective solution against these attacks relies on replacing the real Beacon ID with a temporary replacement called Secure UUID. The exchange happens periodically through an algorithm known only by the Beacon and the server.
Even if the attacker captures a temporary identifier, it can't be used because it’ll expire soon. The algorithm shouldn't be stored in the mobile application because it can be reverse-engineered. This means the mobile application has to communicate with the server to exchange the temporary identifier for a real one.
This solution requires a constant internet connection. In other words, even if your mobile app caches content for offline usage, Beacon-related features will still require internet connectivity. You can make the exchange period longer or allow the application to cache several future identifiers, but these attempts to support offline capabilities come with lower security.
BLE Beacon Use Cases
Beacons are quite useful things that can serve as an informational source or even attract potential customers. Here are some examples of how beacons are used in the modern world:
- In museums and galleries beacons serve as an extended information source. While you're standing next to a famous painting, your device catches a signal from the closest beacon and, if you grant location permission, opens a page devoted to the history of the artist and their creation.
- In retail beacons often serve as an advertising device, notifying about the most interesting deals and discounts. While passing by a store your device catches the signal of a shop’s beacon and transfers you to a page with the newest collections and available disсounts. Moreover, shopping malls use beacons to offer customers GPS-like indoor navigation.
- In educational facilities beacons also serve as a notificator about the upcoming events, conferences, holidays, etc. Once again your device receives a signal with a pre-programmed announcement and grants access to a page with the approaching educational activities listed in one place.
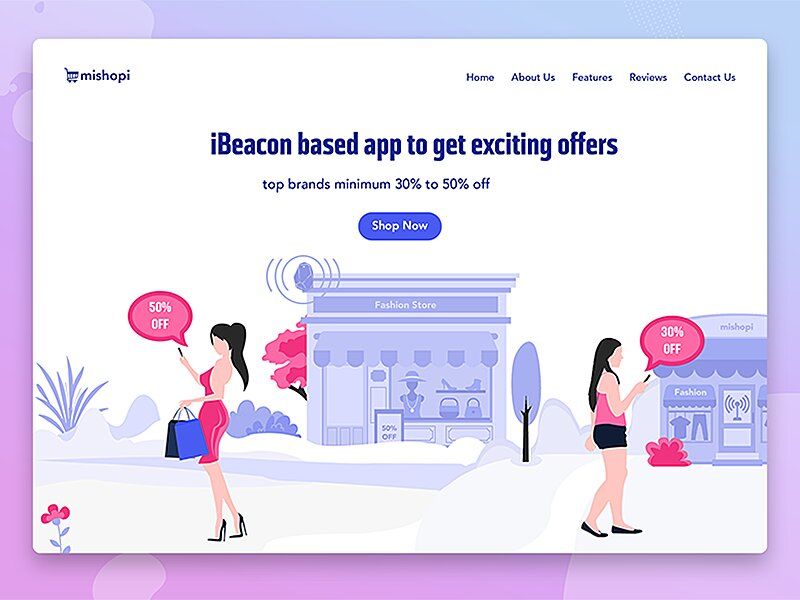
Notifications created by beacons’ continuous signal transmissions (image by 300Mind UI/UX)
What do we know about Beacons and iBeacons? 👇
- BLE beacons are wireless hardware transmitters that broadcast their identifier to nearby smartphone-like devices.
- iBeacon is an Apple protocol based on BLE proximity sensing, similar to a Bluetooth LE protocol stack.
- BLE beacons and iBeacons differ in how they deliver information about the distance between connected products.
- BLE beacons work by constantly transmitting radio signals that are detected by nearby devices with Bluetooth Low Energy support. When a device detects the signal, it sends the ID number to a cloud server, which determines the action associated with the ID and sends a response.
- The effective solution against Beacon attacks is replacing the real Beacon ID with a temporary replacement called Secure UUID.
- BLE beacon use cases include extended information sources in museums and galleries, advertising devices in retail, indoor navigation in shopping malls, and announcements in educational facilities.
🗂 Our Expertise in BLE Integrations
We at Stormotion, as an IoT app development company, have already worked on BLE projects from different industries and fields: fitness, transportation, equipment management and others. We help startups and businesses develop mobile & web apps to manage smart BLE devices from fitness trackers to engines, always with a keen eye on optimizing the IoT app development cost.
Also, we create M2M systems where one device is directly connected to another — for example, when you need to connect a heart rate sensor directly to an exercise machine.
Fitness is one of the industries where BLE devices are used the most. Thus, we’d like to highlight our two relevant cases in this section — PlatoonFit and SportPlus. Both of them required connecting different exercise equipment, sensors and monitors.
Platoon Fit
Platoon Fit is a platform where any user may find various progressive exercises for managing indoor workouts. Along with providing exercise guides, the company pays special attention to video content.
Talking about Bluetooth Low Energy device, our task was to build an MVP that would support fitness tracking devices integration. More specifically, we needed to set up a convenient data transfer between connected heart rate sensors with the Platoon Fit application.
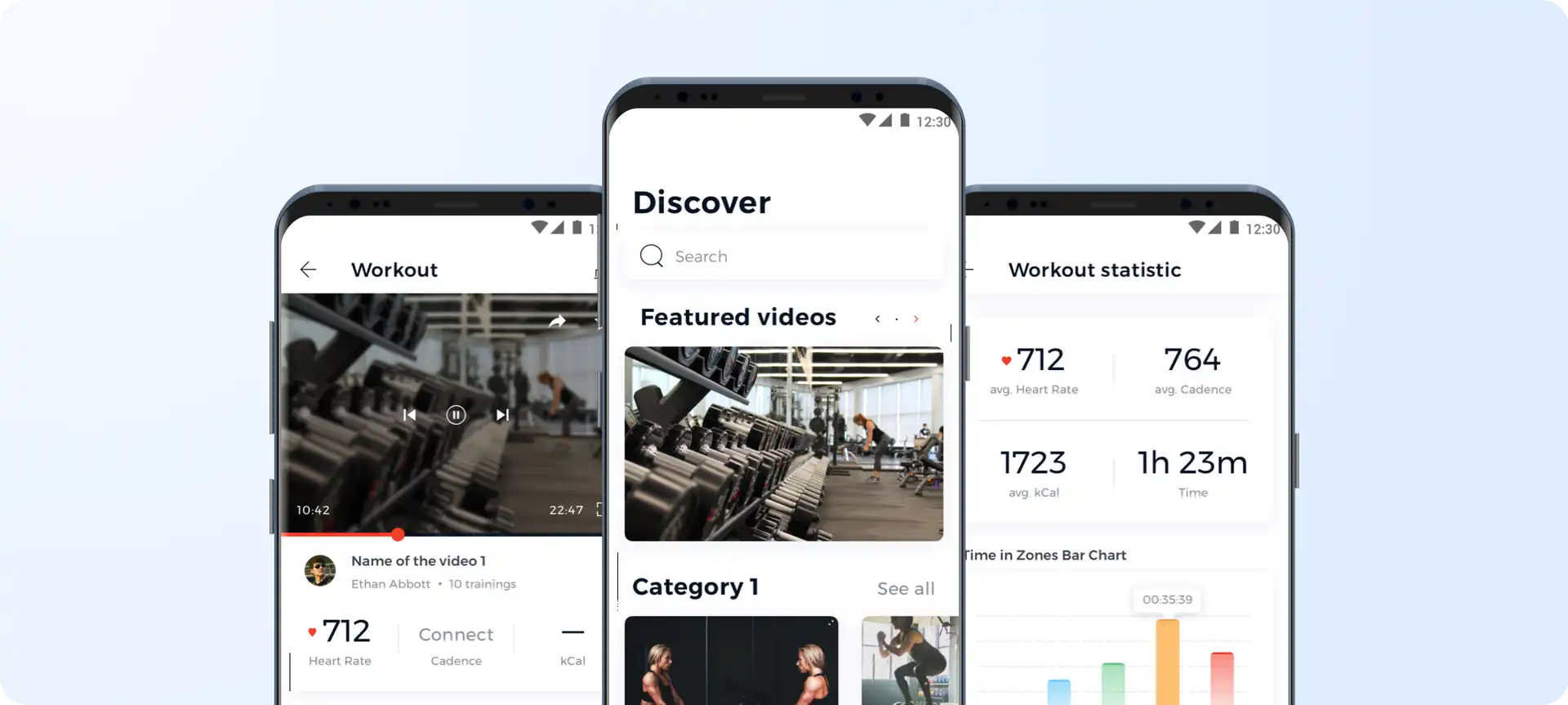
Platoon Fit focuses on health monitoring gadgets as a special part of online workouts (shot by Stormotion)
With the integration of BLE compatibility protocols to the project, we managed to achieve the high-level data transaction system only in 4 weeks of testing and prototyping.
SportPlus
SportPlus is another great specimen on Stormotion’s project showcase. The company produces and sells various unique sports equipment for making their customers’ fitness experience effective. Our task was to design an application that would support every type of exercise machinery they offer.
However, the solution for this case was a challenging one to develop. The challenge lies in the fact that nearly every sports machine the company offers necessitates the use of distinct protocols for exchanged data, which leads us to the main problem. To build a proper communication between an application and the equipment we need to take every possible protocol into account.
With the strategy we created, we managed to access the data flow between another functioning app and the specific machine they offer. Thanks to this decision, we determined the order and format required for sending and receiving different bytes of information in each particular case. After the experimental part, we succeeded in supporting every possible connection for a complete data collection and data exchange system, regardless of the required machinery protocol.
💡 Takeaways
As the topic of BLE products is getting more relevant throughout the years, with the rise of interest there also rises the urge to answer all the frequently asked questions regarding the technology again and again. We at Stormotion tried our best to provide answers to the most common questions in terms of Bluetooth Low Energy and products supported by this technology.
If you have any questions or need any help with integrating Bluetooth Low Energy into your project, let us know. We will be happy to help you meet your business needs with a stunning BLE product!
Our clients say
![Stormotion client David Lesser, CEO from [object Object]](/static/93e047dadd367691c604d8ffd1f54b58/b0e74/david.png)
They were a delight to work with. And they delivered the product we wanted. Stormotion fostered an enjoyable work atmosphere and focused on delivering a bug-free solution.
David Lesser, CEO
Numina
Was it helpful?
Read also